Knowing about your Website small nitty gritty things are always a good start for speed optimization journey; Web Page size is one of those important things.
 The smaller your files are, the faster it will take for the browser to download and serve them to your visitors. Users cannot wait for long for your website content to load in-fact they always expect to get the information they are looking for as quickly as possible, and if they don’t see what they are looking for, they will simply slide to your competitors’ websites.
The smaller your files are, the faster it will take for the browser to download and serve them to your visitors. Users cannot wait for long for your website content to load in-fact they always expect to get the information they are looking for as quickly as possible, and if they don’t see what they are looking for, they will simply slide to your competitors’ websites.
Eager to know how to reduce page weight on your WordPress site?
Let’s start!
In this article we will take you to the basics of page weight, how to check the size, and how to reduce a web page size to boost performance.
Let’s see why Web Page Size is so important that it cannot be ignored?
The size of a web page refers to the amount of data that needs to be transferred from the web server to the user’s browser when the page is requested. Web page size is measured in terms of data size, often expressed in kilobytes (KB) or megabytes (MB). It includes all the resources necessary to display the content, such as HTML files, CSS stylesheets, JavaScript scripts, images, videos, and other multimedia elements.
The size of a web page is critical for several reasons, as it directly impacts the user experience, search engine rankings, and overall performance of the website. Smaller web page sizes generally lead to faster loading times which leads to satisfactory user experience, and better revisits. Web developers and administrators are primarily responsible to optimize web page sizes by considering various techniques like compressing images, lazy loading of content, minifying CSS, minifying Java Scripts, utilizing cookies & browser caching, and opting for content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute content efficiently.
Following are few of the important reasons why web page size cannot be ignored for a fast-running website:
- Loading Speed: Users today expect fast-loading web pages. A large page size can result in slow loading times, leading to a poor user experience. Studies have shown that users are more likely to abandon a website if it takes too long to load.
- Best User Experience: A smaller web page size contributes to a smoother and more enjoyable user experience. Visitors are more likely to stay on a site that loads quickly, reducing bounce rates and increasing user engagement.
 Mobile Responsiveness: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it’s essential for websites to be optimized for various screen sizes and network conditions. Smaller page sizes are crucial for better mobile responsiveness and faster loading on slower mobile networks.
Mobile Responsiveness: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it’s essential for websites to be optimized for various screen sizes and network conditions. Smaller page sizes are crucial for better mobile responsiveness and faster loading on slower mobile networks.- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Search engines like Google consider page speed as a ranking factor. Faster-loading pages are more likely to rank higher in search results, leading to increased visibility and traffic. Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool is one example that evaluates web page performance and provides recommendations for improvement.
- Bandwidth Usage: Smaller page sizes consume less bandwidth, which is especially important for users with limited data plans. This is particularly relevant in regions where internet access is more expensive or less reliable.
- Better Conversion Rates: Faster-loading pages are often associated with higher conversion rates. If visitors can quickly access the content or complete desired actions (such as making a purchase), they are more likely to convert.
- Accessibility: Users with slower internet connections or older devices may struggle to load large web pages. Optimizing page size contributes to better accessibility, ensuring that a wider audience can access and navigate the site.
- User Retention: Users are more likely to return to a website that offers a positive experience. Faster-loading pages contribute to user satisfaction and can help retain visitors over time.
How to Check Your Web Page Size
 The size of a web page is typically measured in terms of its total file size, including all the HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other resources that the page needs to load. Many different techniques can be used for measuring a web page size, for example Developer Tools in Web-browsers, Online tools. To get the quick page information we will explore popular online tools such as GTmetrix, Pingdom and WebPagetest etc. All these tools test the real time web vitals of your website page and gives a credible results in terms of various parameters like Page Size, Performance, Speed etc.
The size of a web page is typically measured in terms of its total file size, including all the HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other resources that the page needs to load. Many different techniques can be used for measuring a web page size, for example Developer Tools in Web-browsers, Online tools. To get the quick page information we will explore popular online tools such as GTmetrix, Pingdom and WebPagetest etc. All these tools test the real time web vitals of your website page and gives a credible results in terms of various parameters like Page Size, Performance, Speed etc.
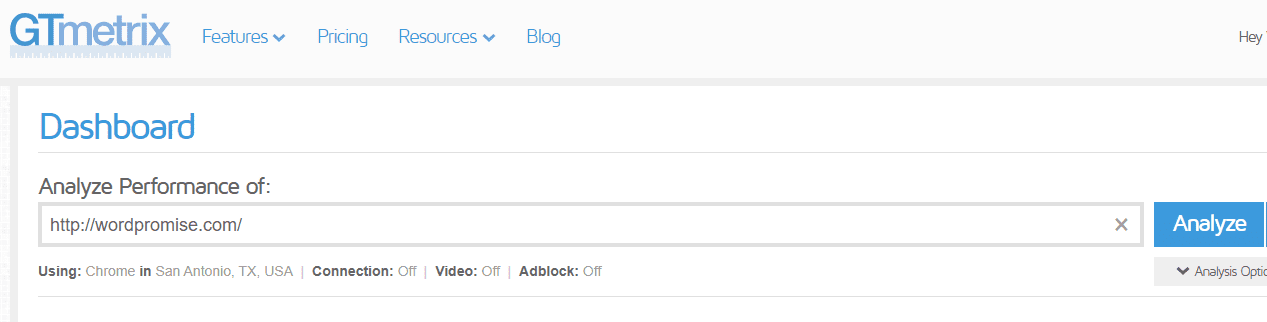
1.Simply enter your website URL into these tools, and they will provide detailed reports on your page’s performance, including size.
GTmetrix
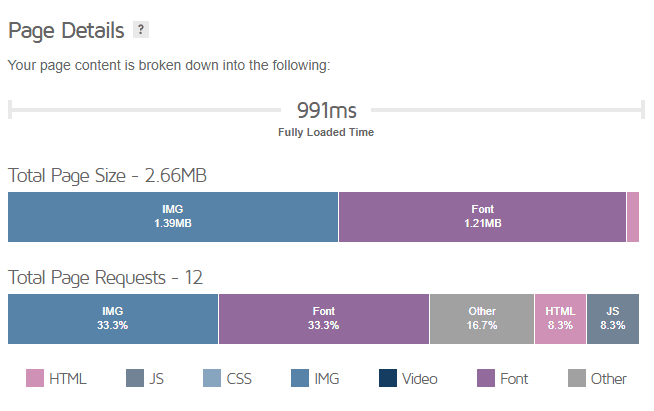
2. Refer the Page Details section: we got 2.66 MB for WordPromise taking less than 1 second time, which is a good score compared to the average worldwide, as shown in the next statistics section.
Similarly, you can refer the Pingdom or WebPagetest tool to get the desired information regarding Page Size.
Pingdom
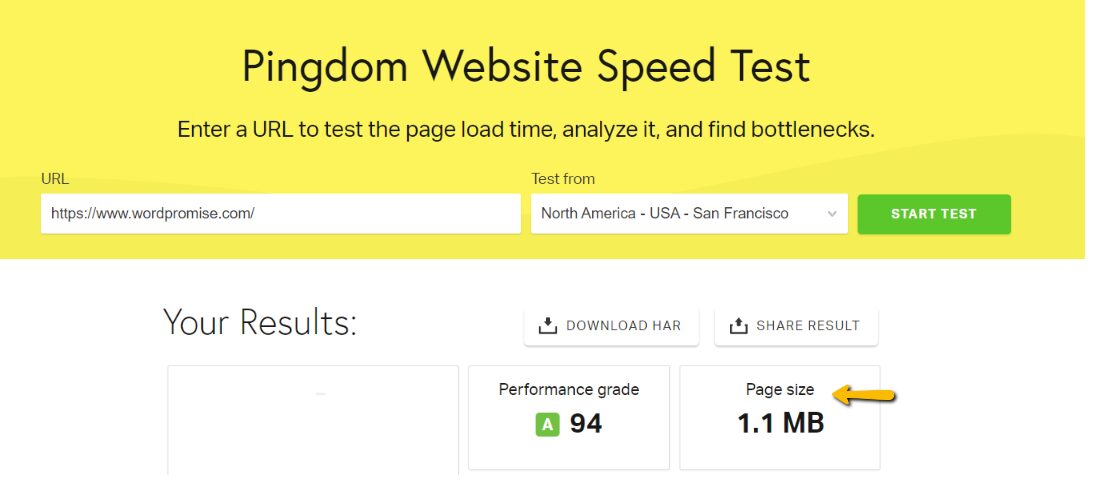
What’s The Ideal Web Page Weight?
The average page size around 1-1.5 MB is reasonable on mobile as well as desktop, the smaller in size is more efficient and ideal. However, if your business demands many images, videos, anything under 3 MB is still OK. Simple thumb of rule is that heavier your page is, harder it will be to optimize it for performance.
How to Reduce Web Page Size (Including HTML)
Here are few important strategies to help you reduce the size of your web pages:
- Optimize Images: Use image compression tools, plugins such as ‘ITheme- Smush’, ’WPRocket’ to reduce the file size of images without significantly sacrificing quality. Consider using modern image formats like WebP, which often provide better compression than traditional formats like JPEG or PNG.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Remove unnecessary white spaces, comments, and line breaks from your CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files. Utilize minification tools, plugins such as ‘WPRocket’ or build processes that automatically minify your code before deployment.
- Combine and Bundle Files: Reduce the number of HTTP requests by combining multiple CSS or JavaScript files into one. Bundle your CSS and JavaScript files to reduce the number of separate files that need to be loaded.
- Use Browser Caching: Configure your server to leverage browser caching. This allows browsers to store copies of static resources locally, reducing the need to download them on subsequent visits.
- Enable Compression: Enable server-side compression (e.g., GZIP etc.) to compress text-based resources before they are sent to the client, reducing transfer time and file size.
- Lazy Load Resources: Implement lazy loading for images and other non-critical resources. This defers the loading of certain elements until they are about to come into the user’s viewport, reducing the initial page load time.
- Optimize Fonts: Use web-safe fonts whenever possible to reduce the need for additional font files. If custom fonts are necessary, consider using tools to subset fonts, including only the characters needed for your website.
- Reduce Redirects: Minimize the use of redirects, as each redirect results in an additional HTTP request and increases page load time.
By combining these strategies as per your website requirements, you can significantly reduce the size of your web pages for a better, improved website performance.
Wrapping Up
To optimize web page size, developers often employ multiple techniques such as image compression, minification of CSS and JavaScript files, lazy loading of media files, and using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to deliver content more efficiently. It’s important for web developers and administrators to regularly monitor and optimize web page sizes to ensure a positive user experience and maintain competitiveness in search engine rankings.
Keep in mind that ongoing monitoring and optimization is very essential for maintaining a fast and efficient website. For more information and queries, you can reach out to us info@wordpromise.com
 Mobile Responsiveness: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it’s essential for websites to be optimized for various screen sizes and network conditions. Smaller page sizes are crucial for better mobile responsiveness and faster loading on slower mobile networks.
Mobile Responsiveness: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it’s essential for websites to be optimized for various screen sizes and network conditions. Smaller page sizes are crucial for better mobile responsiveness and faster loading on slower mobile networks.